# Essential Mathematical Principles Every Programmer Should Know
Written on
Chapter 1: Introduction to Mathematical Foundations
In today's tech-driven world, it is often said, "You don't need math to code." While there is some merit to this notion, a deeper exploration into programming and software architecture reveals that mathematics is fundamentally important. Just as the universe is woven together by physical laws, math forms the backbone of the intricate operations that dictate how computers function.
This paragraph will result in an indented block of text, typically used for quoting other text.
Section 1.1: Boolean Logic: The Core of Programming
Whenever you implement a conditional statement or determine the execution path of your code, you are engaging with Boolean algebra. This binary logic framework relies on ‘True’ and ‘False’ values and employs operators like ‘AND’, ‘OR’, and ‘NOT’. Mastering these basic concepts can simplify even the most complex algorithms.
Section 1.2: Understanding Number Systems
While humans typically use the base-10 number system due to our ten fingers, computers communicate using binary, or base-2, which consists of just 1s and 0s. Gaining familiarity with binary and other numeral systems, such as hexadecimal, is crucial, especially when interacting with hardware or computer memory.
Section 1.3: The Quirks of Floating Point Arithmetic
Computers are designed for accuracy, but they can sometimes produce surprising outcomes due to their method of storing numbers. Floating-point representation, which is used for real numbers, can lead to small inaccuracies. Understanding these nuances can save you significant time spent debugging.

Section 1.4: Logarithmic Functions and Algorithm Efficiency
Logarithms frequently appear in computer science, particularly regarding the efficiency of algorithms. Concepts like binary search and tree data structures rely on logarithmic principles. Recognizing these patterns can enhance performance and scalability.

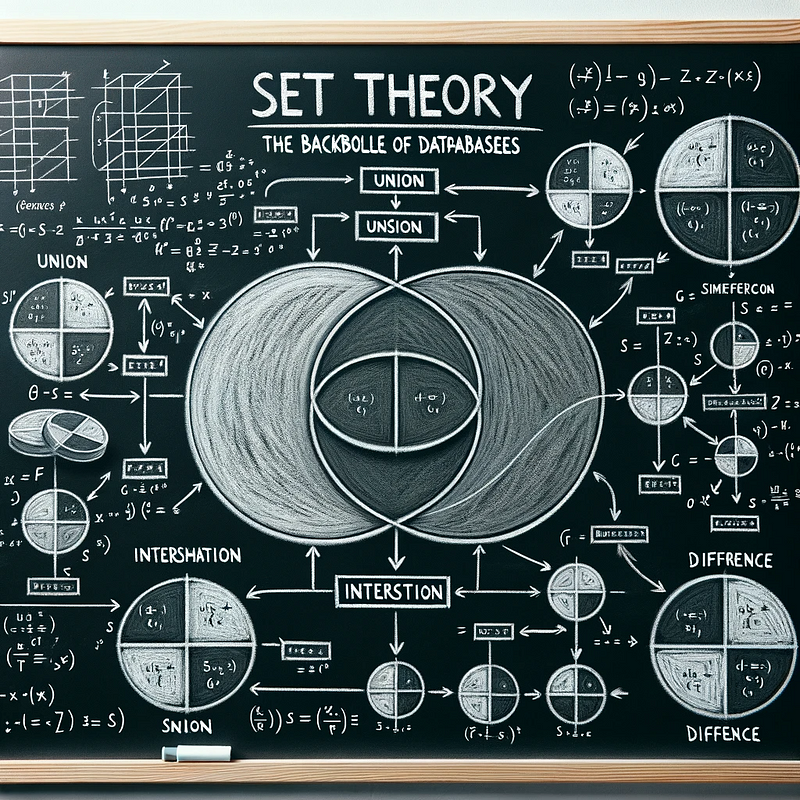
Section 1.5: Set Theory in Database Management
Database technologies, whether SQL or NoSQL, utilize principles from set theory. Concepts such as joins, unions, and intersections are not merely theoretical; they are essential for crafting efficient and accurate database queries.

Section 1.6: Combinatorics: Counting and Probability
From generating various password combinations to predicting user matches on dating applications, combinatorics is invaluable for enumerating potential outcomes. It combines art and science in counting, providing tools for managing complex combinations and permutations.
Section 1.8: Complexity Theory: Assessing Algorithm Efficiency
Before diving into coding, it's essential to evaluate an algorithm's performance. Complexity theory and Big O notation empower developers to make informed decisions regarding optimal algorithms and data structures.

Section 1.9: The Role of Statistics in AI and Machine Learning
Machine learning is not simply magical; it is deeply rooted in mathematics. Statistical concepts underpin predictive modeling, data analysis, and neural networks. The next time you interact with a virtual assistant like Siri or Alexa, remember that robust statistical methodologies are at work.

Section 1.10: Linear Algebra: Creating Virtual Spaces
Linear algebra is essential in fields like gaming graphics, augmented reality, and certain encryption techniques. The manipulation of matrices and vectors is crucial for constructing digital environments and secure systems.

Chapter 2: Visual Learning Aids
The first video titled "10 Math Concepts for Programmers" explores essential mathematical principles that can enhance programming capabilities and understanding in technology.
The second video titled "10 Basic Math Concepts Every Programmer Must Know" provides a foundational overview of critical math concepts that every coder should familiarize themselves with.
Conclusion
Mathematics serves as a universal language, connecting human reasoning with the precision of computer operations. The next time someone claims that math and programming are unrelated, consider the remarkable synergy that occurs when they intersect. If you found this exploration of technological principles enjoyable, please share, like, and follow for more insights into the ever-evolving domain of programming and technology!
